Behind every “overnight success” product is usually a boring—but repeatable—workflow built on data, tools, and disciplined decision-making. Product research tools don’t magically tell you what to sell. What they do is help you eliminate bad ideas faster and validate good ones with confidence.
This guide will walk you through the entire product research process, step by step:
-
From keyword discovery
-
To demand validation
-
To competitor analysis
-
To final product decision-making
No hype. No shortcuts. Just a clear, practical system you can apply immediately.
1. Why Product Research Tools Matter (and Why Most People Use Them Wrong)
1.1 Tools Don’t Find Products—People Do
A common beginner mistake is expecting a tool to say:
“Sell this product. You will make money.”
That never happens.
Tools provide signals, not answers:
-
Search demand
-
Market saturation
-
Price ranges
-
Competitor behavior
Your job is to interpret those signals logically.
1.2 The Real Goal of Product Research
The goal is not to find:
-
The cheapest product
-
The trendiest product
-
The most “cool” product
The real goal is to find a product with:
-
Clear demand
-
Manageable competition
-
Room for differentiation
-
Healthy margins
Every step in this guide supports one of those four criteria.
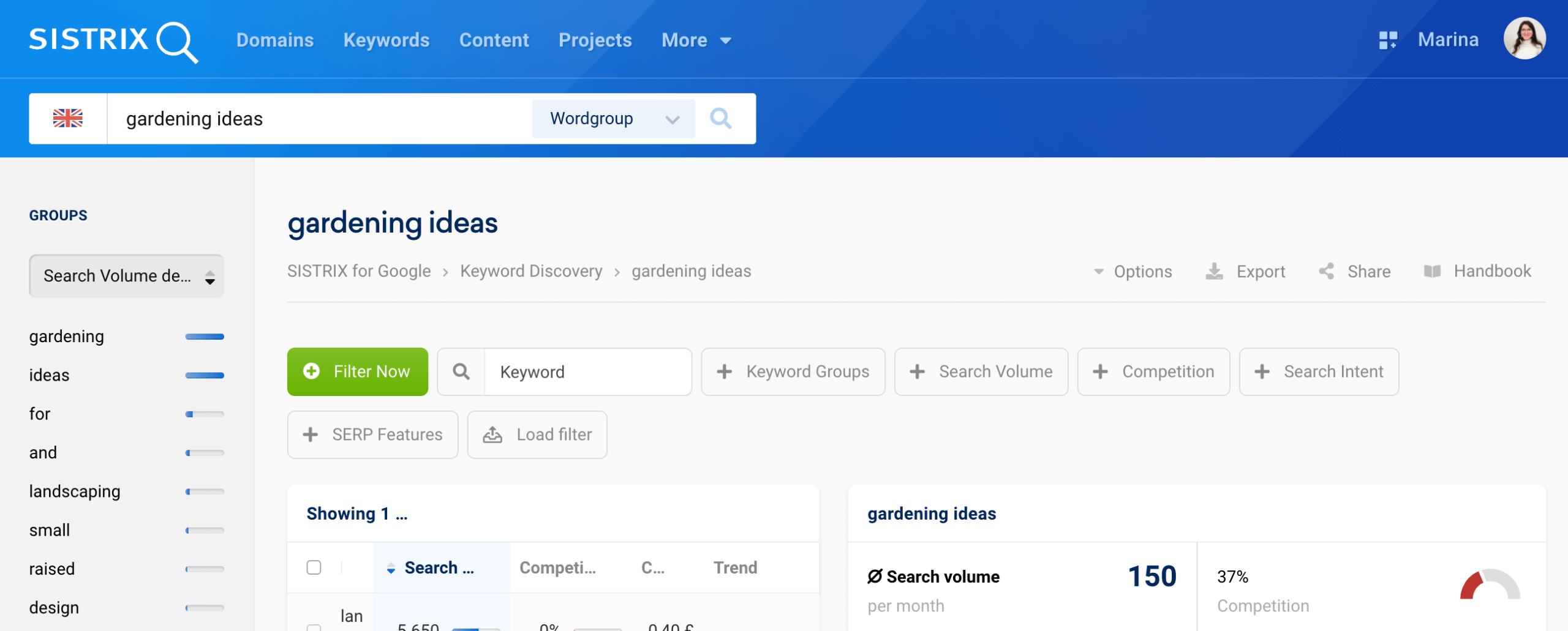
2. Step One: Start With Keywords, Not Products
2.1 Why Keywords Come First
Many beginners start by browsing:
-
Supplier websites
-
TikTok trends
-
“Winning product” videos
That’s backwards.
Keywords represent real buyer intent. If people are searching for something consistently, demand already exists.
2.2 What Makes a “Good” Product Keyword?
A strong product keyword usually:
-
Describes a specific use case
-
Is not overly generic
-
Signals buying intent
Examples:
-
❌ “lamp”
-
✅ “portable camping lantern”
The second keyword tells you:
-
Who the user is
-
Where it’s used
-
Why it’s needed
2.3 Using Keyword Tools Effectively
When using any keyword research tool, focus on:
-
Monthly search volume
-
Keyword trends over time
-
Related keyword clusters
Ignore vanity metrics early on. One keyword rarely tells the full story.
3. Step Two: Expand and Map Keyword Intent
3.1 Build a Keyword Cluster, Not a Single Term
One keyword is a hint.
A cluster is evidence.
For example:
-
“portable UV light”
-
“UV sanitizer for travel”
-
“hotel bed UV sanitizer”
-
“UV light for camping”
Together, they indicate:
-
A specific lifestyle
-
Multiple use cases
-
Repeatable demand
3.2 Classify Keywords by Intent
Split keywords into three groups:
-
Informational – “how to sanitize hotel bed”
-
Comparative – “UV sanitizer vs wipes”
-
Transactional – “buy portable UV sanitizer”
A healthy product niche includes all three.
3.3 Watch for Language Patterns
Pay attention to:
-
Repeated pain points
-
Emotional triggers (safe, clean, portable, easy)
-
Usage scenarios (travel, baby, outdoor, office)
This language later becomes:
-
Product positioning
-
Ad copy
-
Landing page structure
4. Step Three: Validate Demand Beyond Keywords
4.1 Search Volume Is Necessary—but Not Sufficient
High search volume alone doesn’t guarantee:
-
Willingness to pay
-
Repeat purchases
-
Sustainable margins
You must confirm that people are buying, not just searching.
4.2 Cross-Check With Marketplaces
Look at:
-
Amazon search results
-
Best-seller rankings
-
Number of reviews
-
Review growth velocity
If a keyword has demand but no active sellers, that’s a red flag—not an opportunity.
4.3 Price Range Tells a Story
Ask:
-
Are products clustered at one price point?
-
Is there a clear “premium” tier?
-
Are margins realistic after fees and shipping?
Healthy markets allow multiple price tiers.
5. Step Four: Competitor Discovery (Who Are You Really Competing With?)
5.1 Your Real Competitors Are Not Big Brands
Beginners often fear:
-
Amazon basics
-
Famous brands
In reality, your true competitors are:
-
Mid-level sellers
-
Niche brands
-
Optimized listings targeting the same keywords
Those are the benchmarks you must beat.
5.2 How to Identify Core Competitors
Search your main keyword and list:
-
Top organic results
-
Top paid ads
-
Independent brand sites
Ignore outliers. Focus on those consistently visible.
5.3 Build a Competitor Snapshot
For each competitor, note:
-
Price
-
Core features
-
Product variations
-
Review count
-
Messaging angle
Patterns will emerge quickly.
6. Step Five: Deep Competitor Analysis (Where They Win—and Where They Fail)
6.1 Read Reviews Like a Product Manager
Don’t just read 5-star reviews.
Focus on:
-
3-star and 4-star reviews
-
Repeated complaints
-
“I wish it had…” statements
These are built-in product improvement ideas.
6.2 Analyze Visual and Content Gaps
Ask:
-
Are product images clear?
-
Is usage demonstrated?
-
Is the value proposition obvious?
Poor presentation is often a bigger weakness than the product itself.
6.3 Feature Overlap vs Differentiation
List:
-
Must-have features (table stakes)
-
Nice-to-have features
-
Missing features competitors ignore
Your product doesn’t need to be revolutionary—just clearly better in one or two areas.
7. Step Six: Market Saturation—How Much Is Too Much?
7.1 Saturation Is Not Binary
Markets aren’t simply:
-
Saturated
-
Unsaturated
They exist on a spectrum.
A “crowded” market can still be profitable if:
-
Messaging is weak
-
Branding is generic
-
User needs are underserved
7.2 Signs of Dangerous Saturation
Be cautious if:
-
All products look identical
-
Prices are racing to the bottom
-
Ads rely only on discounts
-
No brand storytelling exists
These signal margin pressure.
7.3 Signs of Healthy Competition
Healthy markets show:
-
Different positioning angles
-
Price diversity
-
Ongoing product innovation
Competition validates demand.
8. Step Seven: Product Viability Checklist
Before committing, confirm:
-
Demand is consistent (not a spike)
-
Competition is beatable
-
Differentiation is realistic
-
Supply chain is stable
-
Margins survive ads and returns
If even one factor fails, walk away.
9. Turning Research Into Action
9.1 From Data to Decision
At this stage, your question changes from:
“Is this a good product?”
To:
“Can I win with this product?”
That depends on:
-
Your branding skill
-
Your marketing channel
-
Your budget and patience
9.2 Document Everything
Keep records of:
-
Keyword clusters
-
Competitor notes
-
Pricing benchmarks
-
Feature decisions
This turns product research into a repeatable system—not a one-time guess.
10. Common Beginner Mistakes to Avoid
-
Falling in love with a product before research
-
Ignoring negative data
-
Overestimating differentiation
-
Copying competitors exactly
-
Rushing to launch without validation
Tools reveal reality. Don’t argue with it.
Final Thoughts: Product Research Is a Skill, Not a Trick
The best sellers don’t “get lucky” repeatedly.
They:
-
Follow process
-
Trust data
-
Kill weak ideas early
-
Refine strong ones patiently
Product research tools are only as powerful as the workflow behind them.
Master the workflow—and the tools simply become extensions of your judgment.
And that’s when product selection stops feeling risky—and starts feeling controlled.



 7 min read
7 min read