As global e-commerce continues to expand, staying compliant with local tax regulations is becoming increasingly essential for businesses. Among the most important tax systems that affect cross-border sales in the European Union are VAT, OSS, and IOSS. These systems not only ensure compliance but also help businesses streamline their operations and avoid costly mistakes.
In this article, we will break down what VAT, OSS, and IOSS are, how they work, and how understanding these frameworks can help you stay ahead in the global e-commerce game as we approach 2025.
Here’s an table with Standard VAT Rate for some important countries:
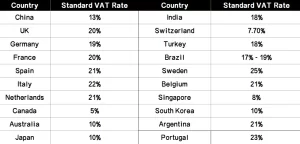
Note: The United States does not have VAT; it only has sales tax. Sales tax is levied only at the retail stage, unlike in most countries where taxes are applied to the value added at each stage of the supply chain.
Contents
ToggleWhat is VAT ?

VAT is charged at each stage of the supply chain, including production, wholesale, and retail. At every stage, tax is applied to the “added value” of goods and services. The “added value” refers to the extra value created at each stage, like processing, transforming, transporting, and distributing the product.
Example: Let’s say you’re a toy factory. You make a toy and sell it to a store. The store then sells it to a customer. At each step, from production to sale, a small tax is added. But each person only pays VAT on the “added value” they created, not the entire product.
Let’s walk through the process:
Assume you buy a television at an electronics store, priced at 500 euros. The VAT rate is 20%.
1.Merchant Purchase (Wholesaler)
The merchant purchases the television from a supplier at a price of 300 euros (excluding VAT).
The VAT paid on the purchase is 300 euros * 20% = 60 euros.
Therefore, the merchant actually pays the supplier a total of 300 euros + 60 euros = 360 euros.
2.Merchant Sale (Retailer)
The merchant then sells the television to you for 500 euros (excluding VAT).
The VAT charged to you is 500 euros * 20% = 100 euros.
So, you pay the merchant a total of 500 euros + 100 euros = 600 euros.
3.Merchant’s Tax Handling
The merchant collects 100 euros in VAT from you, but he already paid 60 euros in VAT when purchasing the television.
Therefore, the merchant needs to pay the tax authorities 100 euros – 60 euros = 40 euros.
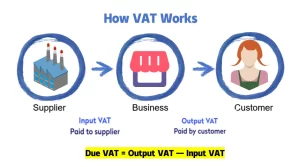
Summary of VAT Calculation Formulas:
● VAT (at each stage) = Sales Price × Tax Rate
● Total Sales Price = Sales Price + VAT
● Actual Payment Price = Sales Price + VAT – Already Paid VAT (deducted)
These formulas simplify the calculation of VAT at each step in the supply chain, ensuring clarity in how VAT is applied and deducted.
Who Should Use VAT?
● VAT-Registered Businesses
In most countries, if you are a legally operating business and your annual sales exceed a certain threshold, you must register and use VAT.
This applies to companies that provide goods or services, such as manufacturers, retailers, wholesalers, and service providers.
● Consumers
The end consumer is the “actual payer” of VAT. While businesses collect VAT, the cost is ultimately included in the price of goods or services and borne by the consumer.
What is OSS?
The EU introduced a simplified VAT filing and payment system called the “One-Stop-Shop” (OSS). With OSS, you only need to register for VAT in one EU country, rather than registering separately in each country where you sell.
For example, if your company is already VAT-registered in Germany, you can use the OSS system to file and pay VAT for all your cross-border sales in France, Italy, and Spain through the German tax authorities. This means you don’t need to register and submit VAT returns in each country; all VAT payments are handled through Germany’s tax office.
How does OSS work?
1.Registration: Businesses need to register for OSS with the tax authorities of an EU member state. EU businesses can choose to register in their home country, while non-EU businesses must register in one EU member state. After registration, you will receive an OSS VAT number.
2.VAT Collection: Even though VAT is declared through the OSS system, you still need to charge VAT based on the rates of each EU country where you sell. For example, when selling goods in France, Germany, or Italy, you must charge VAT according to the local VAT rate of each country.
3.VAT Declaration and Payment: Every quarter, businesses need to submit a VAT return electronically, listing the sales and VAT collected for each EU country. You will then pay the total VAT in one place. The tax authorities will forward the payments to the relevant countries.
Example: Suppose you sold two items—one to France and one to Germany:
For the sale to France, you would charge French VAT at the applicable rate.
For the sale to Germany, you would charge German VAT at the applicable rate.
After collecting these VAT amounts, you submit a single VAT return through the OSS system, and pay the total VAT. The payments will be distributed to the French and German tax authorities accordingly.
Example Calculation for OSS:
● Sale to France:
Sale amount: 100 EUR
VAT (20%): 100 × 20% = 20 EUR
● Sale to Germany:
Sale amount: 100 EUR
VAT (19%): 100 × 19% = 19 EUR
You will submit this information on the OSS platform and pay
the total VAT:20 EUR + 19 EUR = 39 EUR.
The OSS system will then distribute the VAT payments to the tax authorities of France and Germany accordingly.
What is IOSS?
IOSS (Import One-Stop Shop) is a new policy introduced by the EU to simplify VAT (Value Added Tax) declaration and payment for cross-border e-commerce imports. It allows merchants to pay VAT directly to the EU tax authorities when goods are imported, instead of requiring consumers to pay VAT upon receipt of the goods.
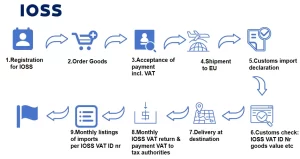
IOSS applies only to low-value goods, meaning items priced below 150 euros each.
For example, if you sell an item for 120 euros (excluding VAT), using the IOSS system, you can pay VAT to the tax authorities when the goods enter the EU. The consumer does not need to pay any additional VAT when receiving the item.

How does IOSS work?
1.Merchant Registers for IOSS: The merchant registers for IOSS in an EU member state and obtains an IOSS number.
2.VAT Calculation at the Time of Sale: The merchant calculates and collects VAT based on the consumer’s country of residence (for example, a 100-euro product sold in France with a 20% VAT would have 20 euros in VAT).
3.Merchant Pays VAT: The merchant pays the collected VAT to the EU tax authorities through the IOSS system.
4.VAT Exemption Upon Import: When the goods enter the EU, the VAT already paid is considered settled, and the consumer does not need to pay VAT at customs.
5.Unified Reporting: The merchant submits a single VAT report through the IOSS system, eliminating the need for separate declarations in each EU country.
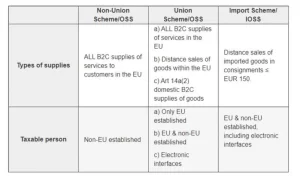
The differences between OSS and IOSS
Here’s a table summarizing the differences between OSS (One-Stop Shop) and IOSS (Import One-Stop Shop) in the context of the EU VAT system:
As we move toward 2025, being well-versed in these tax systems will position your business to thrive in the competitive world of cross-border e-commerce. Make sure to stay informed, adapt your strategies, and leverage these systems to remain at the forefront of global e-commerce.



 8 min read
8 min read











