
If you’re starting a dropshipping business, Shopify and WordPress are two popular platforms to choose from. Both have their strengths and weaknesses, but the right one depends on your skills, business needs, and future plans. Let me break it down in simple terms to help you decide.
Shopify: Easy and Perfect for Beginners
Shopify is made for e-commerce, and it’s super simple to use. Don’t know coding? No problem! Shopify has tons of ready-to-use templates. It’s like building with Lego blocks—you just drag, drop, and create your store. It comes with built-in tools for payments, shipping, and managing orders. This saves you time and lets you focus on selling.
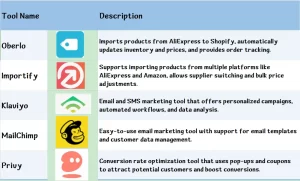
Shopify also has a massive app store. You’ll find tools like Oberlo and Importify to quickly add products, Klaviyo and MailChimp for email marketing, and Privy or Upsell to boost sales. These apps make dropshipping smooth and stress-free.
But Shopify isn’t cheap. The basic plan starts at $29/month, and as your store grows, you might pay more, especially if you use third-party payment gateways. Also, if you want very specific designs or functions, Shopify can feel limiting.
WordPress: Flexible and Powerful, but Needs Tech Skills

WordPress, on the other hand, is a powerful option if you want more control. By adding the WooCommerce plugin, you can turn WordPress into a full e-commerce platform. The biggest advantage? Flexibility. You can design your store however you like and customize features such as payment methods or shipping options.
WordPress is open-source, meaning there are endless plugins and resources available. It’s also cheaper—just pay for hosting and a domain, which costs less than Shopify’s monthly fees.
But here’s the catch: WordPress is not beginner-friendly. If you’re not tech-savvy, setting up plugins, payment systems, and optimizing your site can be overwhelming. And when things go wrong, there’s no centralized support. You’ll need to figure it out yourself or rely on online forums.
Who Should Choose Shopify?
Shopify is perfect if you’re new to e-commerce or want to start fast. It’s simple, has everything you need in one place, and their support team is always there to help. You can focus on selling without worrying about technical stuff.
Who Should Choose WordPress?
Go with WordPress if you know a bit about websites or don’t mind learning. It’s highly customizable and great for unique designs or features. Plus, it’s cheaper long-term. If you’re planning to scale and want full control, WordPress is a smart choice.
Which Platform Has Lower Long-Term Costs: Shopify or WordPress?

When comparing Shopify and WordPress, WordPress generally has lower long-term costs, especially if you manage your site efficiently. Here’s why:
WordPress: Lower Long-Term Costs
No Ongoing Subscription Fees
WordPress itself is free. You’ll only pay for hosting (starting around $5–$15/month), a domain (around $10–$20/year), and any plugins or themes you choose to add. Many plugins are free or have affordable one-time fees.
Customizable for Budget
WordPress allows you to scale costs based on your needs. If you’re on a budget, you can use free plugins and themes. As your business grows, you can invest in premium tools without paying a fixed monthly fee.
No Transaction Fees
WordPress doesn’t charge transaction fees unless you use certain payment gateways that have their own fees. You’ll save more as your revenue grows.
Shopify: Higher Costs Over Time
Monthly Subscription Fees
Shopify starts at $29/month and can go up to $299/month for advanced plans. These fees are unavoidable as long as you use the platform.
Transaction Fees
If you use a third-party payment gateway (like PayPal or Stripe), Shopify takes an additional transaction fee (0.5%–2%), which can add up as your sales increase.
App Costs
Many Shopify apps require monthly fees, and these can stack up quickly if you need multiple tools for your store.
Final Advice
If you’re a beginner, Shopify is the way to go—easy, quick, and hassle-free. If you’re more experienced or willing to learn, WordPress gives you more flexibility and control. Either way, pick the one that fits your needs, and take the first step toward building your dropshipping business. Success is waiting for you!



 5 min read
5 min read











