In the ever-changing landscape of international trade, cross-border e-commerce is seizing unprecedented development opportunities. The dropshipping model, with its low start-up barrier and financial cost advantages, is gradually becoming a popular choice among e-commerce entrepreneurs. Sellers do not need to pre-stock inventory or rent warehouses, but can instead focus solely on product promotion and sales, while suppliers handle production and shipping, significantly reducing initial risks.
However, while enjoying the convenience of dropshipping, cross-border e-commerce also faces a complex and dynamic international market and regulatory environment. Varying consumer preferences and regulatory requirements across countries make compliance operations key to ensuring robust business development. Only by strictly adhering to all regulations can sellers effectively manage risks and achieve long-term success.
This article will explore compliance operation methods for cross-border e-commerce dropshipping, analyze the model’s advantages and potential risks in detail, and provide you with practical compliance recommendations.
What is Dropshipping?
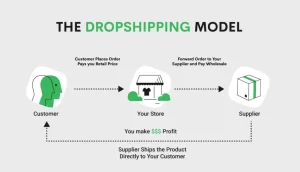
Dropshipping is a retail model where the seller (also known as the dropshipper) does not directly hold or manage inventory. In this model, the seller showcases products on an online store or e-commerce platform. Once a customer places an order, the seller forwards the order details directly to the supplier or manufacturer. The supplier or manufacturer then ships the product directly to the customer.
So, what are the advantages of dropshipping?
Imagine you are the owner of an online clothing store. You don’t need to rent a warehouse to store thousands of pieces of clothing or worry about unsold inventory. Instead, you simply display photos and descriptions of the clothing on your website, and once a customer orders, you notify the supplier to ship the product. This is the freedom that the dropshipping model offers.
Additionally, when a customer sees an item on your website and places an order, the order information is immediately relayed to your supplier. The supplier then picks the product from their warehouse based on the order details and ships it directly to the customer. This process is fast and efficient, reducing intermediaries and improving response times.
In the dropshipping model, your profit comes from the difference between the selling price and the supplier’s wholesale price. For example, if the wholesale price of an item is $20 and you sell it for $40, once the customer places an order, you pay $20 to the supplier and keep the remaining $20 as profit. This model enables you to make sales with minimal upfront costs.
Compliance in Operation: Key Points for Dropshipping in Cross-Border E-commerce
When operating a dropshipping business in cross-border e-commerce, compliance is critical. To conduct your business legally and in accordance with regulations, please consider the following points:
Avoid Infringing Intellectual Property Rights
Unauthorized use of another party’s brand name or trademark
This refers to the use of another party’s brand name, logo, or trademark without obtaining proper authorization. Whether it’s on product packaging, promotional materials, or website displays, using protected brand elements may confuse consumers into mistakenly believing that the product is associated with a well-known brand. Such actions not only harm the reputation of the original brand but may also lead to legal disputes, resulting in high compensation and administrative penalties for the company.

Selling Products That Are the Same or Similar to Popular Brands
Selling items with a highly similar appearance, design, or style to those of popular brands can easily mislead consumers into believing that the products are genuine or officially licensed. Even if the product quality differs, an overly similar design may infringe on the original brand’s design rights or patents, potentially leading to legal disputes. Once consumers’ trust in authentic products is undermined, it not only damages the brand’s image but also disrupts market competition, resulting in significant economic losses and reputational crises.
Sourcing Products from Unregulated Channels
Purchasing products through unregulated channels often lacks proper documentation of legitimate sourcing. This increases the likelihood that the products are counterfeit, substandard, or of poor quality. Selling such products not only causes direct economic and safety losses for consumers but also exposes the business to infringement and fraud risks. Regulatory authorities impose strict penalties on counterfeit and substandard products, and businesses may face severe sanctions, potentially leading to the collapse of their commercial reputation and brand image.
Selling Products with Copyrighted Designs
Using copyrighted design elements in the production and sale of products without authorization constitutes direct infringement. For example, printing Disney characters or other well-known copyrighted images on items such as T-shirts and hats without permission can easily lead consumers to assume that the product has official endorsement. Such actions not only severely violate the legal rights of the copyright holders but, once discovered, may result in lawsuits with heavy compensatory damages and market bans, among other adverse consequences.
Recommendations to Avoid Infringement Risks
In actual business operations, to avoid legal risks and commercial losses associated with intellectual property infringement, it is essential to verify the credentials of your suppliers. Businesses should ensure that suppliers possess valid business licenses, brand authorization certificates, and other relevant documents, thereby reducing the risk of procuring infringing products. Before listing products for sale, it is advisable to have thorough communication with suppliers, clearly conveying the intention to sell products through overseas online channels and discussing related intellectual property issues in detail, ensuring that both parties have a clear understanding of their responsibilities and obligations.
Additionally, tools such as Google’s “reverse image search” can be utilized to compare product appearances and designs to detect any high similarity to well-known brands, thus identifying potential infringement risks early. If there is any uncertainty during information gathering and assessment, it is important to consult with a professional lawyer familiar with the relevant laws and regulations. A lawyer can not only interpret specific intellectual property laws but also assist the business in formulating compliant sales strategies, ensuring that all applicable intellectual property laws and standards in foreign markets are adhered to, thereby safeguarding the business’s legal rights and market competitiveness.

Common Behaviors That Harm Consumer Rights
Abusing Consumer Personal Information
The personal information provided by consumers during the shopping process is sensitive data and should not be misused. Some sellers may use consumer information for unauthorized marketing activities or sell it to third parties, thereby infringing on consumers’ privacy rights. To protect consumer privacy, sellers should clearly inform consumers of the purpose when collecting information and obtain their consent to receive marketing emails. Additionally, providing a clear link to the privacy policy on the platform ensures that the handling of information is transparent and secure.
Implementing Unreasonable Return and Exchange Policies and Concealing Costs


 13 min read
13 min read