In the fast-paced world of dropshipping, product selection tools make it easier than ever to discover trending items, identify profitable niches, and quickly launch new products. However, many beginners face a common dilemma: just because a product looks promising in a selection tool doesn’t mean it’s safe to sell.
What if the supplier delivers poor quality? What if shipping times are unreliable? What if customers complain about defects or false advertising?
Choosing the wrong product can lead to refunds, negative reviews, damaged brand reputation, and financial losses. That’s why experienced sellers never rely solely on data from product research tools. Instead, they verify product quality through multiple dimensions before listing items in their stores.
This guide will walk you through a comprehensive, multi-layered process to validate product quality, supplier reliability, and long-term market potential—so you can sell confidently and build a sustainable dropshipping business.
Why Product Verification Matters in Dropshipping
Dropshipping removes the need to hold inventory, but it also removes direct control over product quality. Unlike traditional retail, you don’t see or handle products before customers receive them.
This creates several risks:
-
Poor manufacturing quality
-
Misleading product descriptions
-
Unreliable suppliers
-
Long or inconsistent shipping times
-
High return rates
-
Negative customer experiences
A single bad product can result in:
-
Increased refund requests
-
Payment disputes
-
Store account restrictions
-
Advertising losses
-
Damaged brand trust
Product verification protects you from these risks and helps ensure long-term profitability.
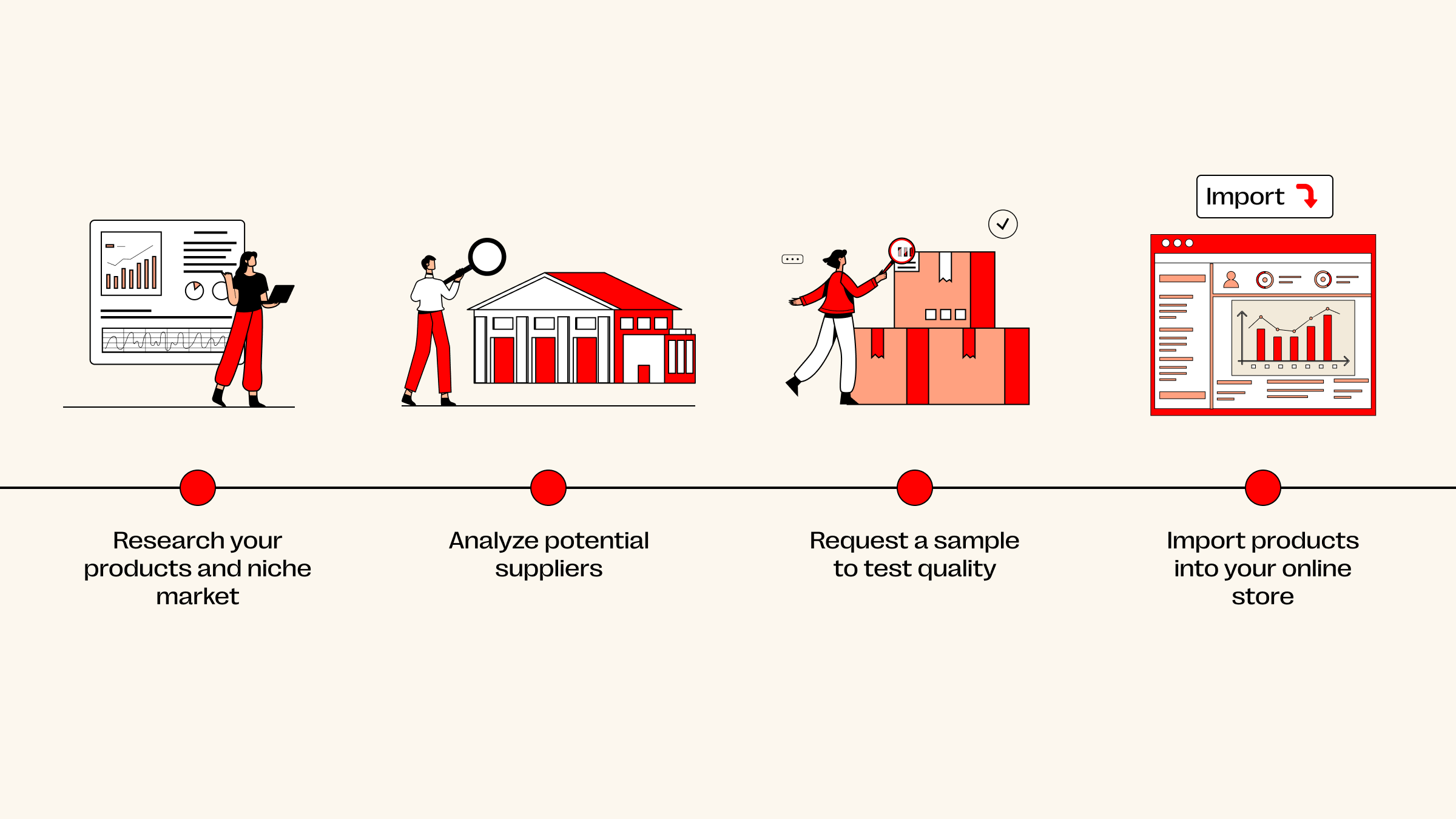
Step 1: Validate the Supplier’s Credibility
Your supplier is just as important as your product. Even a great product can fail if the supplier is unreliable.
Check Supplier History and Experience
Look for:
-
Years in business
-
Transaction volume
-
Customer ratings
-
Manufacturing capabilities
-
Certifications
-
Business licenses
Suppliers with a long track record usually have stable production processes and better quality control.
Analyze Customer Feedback
Don’t just look at the rating score—read the actual reviews.
Pay attention to:
-
Comments about durability
-
Packaging quality
-
Product accuracy vs description
-
Shipping reliability
-
After-sales service
If multiple customers report the same issue, treat it as a warning sign.
Evaluate Communication Speed
Contact the supplier and ask questions:
-
How fast do they respond?
-
Are answers detailed or generic?
-
Do they understand your needs?
Reliable suppliers communicate clearly and quickly.
Step 2: Order Samples Before Selling
Professional sellers always test products themselves.
Why Sample Testing Is Essential
Sample testing helps you verify:
-
Build quality
-
Material durability
-
Packaging standards
-
Product functionality
-
Actual appearance vs listing photos
It also lets you evaluate the full customer experience—from ordering to delivery.
What to Test in a Sample
When your sample arrives, inspect:
-
Product design and finish
-
Strength and durability
-
Safety features
-
Ease of use
-
Packaging protection
-
Accuracy of description
Document your findings carefully.
Test Real Usage Conditions
Use the product like a real customer would:
-
Test performance repeatedly
-
Try extreme conditions if relevant
-
Check for wear over time
This reveals potential issues that initial inspection may miss.
Step 3: Analyze Product Materials and Manufacturing Quality
Understanding how a product is made helps predict long-term reliability.
Evaluate Materials
Look for:
-
High-grade plastics vs cheap materials
-
Metal strength and thickness
-
Fabric quality
-
Surface finishing
-
Weight consistency
Premium materials usually result in fewer returns and better customer satisfaction.
Examine Build Precision
Signs of good manufacturing include:
-
Smooth edges
-
Tight assembly
-
Uniform color
-
No loose components
-
Consistent measurements
Poor precision often indicates weak quality control.
Step 4: Compare Multiple Suppliers
Never rely on just one supplier.
Why Comparison Matters
Different suppliers may sell similar products with different quality levels. Comparing options helps you identify the best balance of:
-
Price
-
Quality
-
Shipping speed
-
Reliability
How to Compare Effectively
Order samples from multiple suppliers and compare:
-
Material quality
-
Packaging
-
Product consistency
-
Delivery time
-
Communication experience
Choose the supplier that provides the best overall value—not just the lowest price.
Step 5: Evaluate Shipping Performance
Shipping quality directly affects customer satisfaction.
Test Delivery Speed
Measure:
-
Processing time
-
Shipping duration
-
Tracking reliability
Unpredictable delivery creates complaints and refund requests.
Inspect Packaging Protection
Poor packaging leads to damaged products.
Look for:
-
Protective materials
-
Secure sealing
-
Damage resistance
-
Professional presentation
Packaging quality reflects the supplier’s attention to detail.
Step 6: Research Market Feedback Across Platforms
Customer feedback from multiple sources reveals real product performance.
Check Online Reviews
Search for the product across:
-
E-commerce platforms
-
Forums
-
Social media discussions
-
Video reviews
Look for consistent complaints or praise.
Identify Common Issues
Recurring problems might include:
-
Battery failure
-
Fragile parts
-
Incorrect sizing
-
Poor instructions
-
Low durability
Frequent issues suggest quality risks.
Step 7: Test Return and Refund Processes
A reliable supplier supports your business even when problems occur.
Ask About Return Policies
Verify:
-
Replacement process
-
Refund conditions
-
Defect handling
-
Warranty options
Clear policies reduce risk.
Simulate After-Sales Communication
Send support questions and evaluate:
-
Response speed
-
Professionalism
-
Problem-solving ability
Good after-sales service protects your reputation.
Step 8: Verify Product Compliance and Safety Standards
Certain products must meet safety or regulatory requirements.
Check Certifications
Depending on product type, verify:
-
Electrical safety certifications
-
Material safety standards
-
Environmental compliance
-
Consumer protection regulations
Compliance reduces legal and platform risks.
Step 9: Evaluate Long-Term Supplier Stability
You want a supplier who can support long-term growth.
Assess Production Capacity
Ask about:
-
Manufacturing scale
-
Inventory stability
-
Customization capability
-
Peak season readiness
Supply shortages can disrupt your business.
Check Business Consistency
Look for:
-
Stable pricing
-
Reliable restocking
-
Consistent quality batches
Consistency ensures predictable operations.
Step 10: Conduct Small-Scale Market Testing
Before scaling, test demand and customer satisfaction.
Launch a Trial Campaign
Sell limited quantities to evaluate:
-
Customer reactions
-
Return rates
-
Review feedback
-
Support requests
Analyze Performance Metrics
Track:
-
Conversion rate
-
Refund percentage
-
Customer satisfaction
-
Product complaints
Use data to decide whether to scale.
Step 11: Monitor Product Performance Continuously
Verification doesn’t stop after launch.
Track Customer Feedback
Regularly review:
-
Product reviews
-
Customer emails
-
Support tickets
-
Return reasons
Maintain Supplier Communication
Stay in touch with suppliers to:
-
Address quality issues
-
Improve packaging
-
Upgrade materials
-
Adjust specifications
Continuous monitoring ensures long-term success.
Step 12: Use Data Tools for Ongoing Quality Insights
Modern sellers combine manual verification with data analytics.
Monitor Market Trends
Track:
-
Sales trends
-
Demand fluctuations
-
Competitor performance
-
Price changes
Analyze Competitor Stores
Observe:
-
Customer reviews
-
Product updates
-
Complaint patterns
-
Quality improvements
This provides valuable industry insights.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Choosing the Cheapest Supplier
Low price often means compromised quality.
Skipping Sample Testing
Relying on photos or descriptions is risky.
Ignoring Negative Reviews
Small issues can become major problems.
Scaling Too Quickly
Test before investing heavily in advertising.
Building a Reliable Product Selection Workflow
Successful dropshipping businesses follow a structured process:
-
Identify trending products using research tools.
-
Validate supplier credibility.
-
Order and test samples.
-
Compare suppliers.
-
Verify shipping and packaging.
-
Research market feedback.
-
Test customer response.
-
Monitor ongoing performance.
This workflow minimizes risk and maximizes profitability.
The Competitive Advantage of Quality Verification
Many beginners chase trends blindly. Professional sellers focus on reliability and customer satisfaction.
When you verify product quality thoroughly, you gain:
-
Higher customer trust
-
Lower refund rates
-
Better reviews
-
Stronger brand reputation
-
Sustainable profit growth
Quality verification is not extra work—it’s a strategic advantage.
Final Thoughts
Product research tools make discovering opportunities easier than ever, but true success in dropshipping depends on what happens after discovery. Verifying product quality through supplier evaluation, sample testing, material inspection, shipping analysis, and market validation ensures you sell products customers love.
Instead of asking, “Is this product trending?” experienced sellers ask, “Is this product reliable, consistent, and worth selling long term?”
By adopting a multi-dimensional verification strategy, you protect your business, build trust with customers, and create a foundation for sustainable e-commerce growth.
The most profitable dropshipping stores are not built on quick wins—they’re built on careful decisions, rigorous testing, and unwavering commitment to quality.


 8 min read
8 min read